Liam Jones, SoCoBio graduate, is excited to share the latest publication from his PhD research, building on previous work using a dual anaerobic reactor model to study biofilm-mediated microbiologically influenced corrosion (MIC) on carbon steel. In collaboration with DNV, this study tackled a critical industry challenge: How effective are conventional biocides like glutaraldehyde under realistic, mixed-species biofilm conditions?
Here’s what they found:
- Despite biocide treatment, biofilms persisted and continued to cause localized corrosion, highlighting incomplete mitigation.
- Biocide application caused an electronegative shift in Ecorr and reduced H₂S concentrations, indicating partial microbial suppression.
- Raman spectroscopy and profilometry revealed distinct differences in corrosion product composition and pit morphology between biotic and abiotic systems.
- 16S rRNA sequencing showed enrichment of stress-tolerant genera, Exiguobacterium and Serpentinicella, suggesting chemical resilience within the biofilm.
These results underscore the limitations of traditional biocide strategies and the urgent need for adaptive, community-informed treatments. Our dual anaerobic biofilm reactor offers a reproducible platform for future MIC standardization and deeper mechanistic investigations under environmentally relevant, anoxic conditions.
Link to read publication here: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41529-025-00628-0
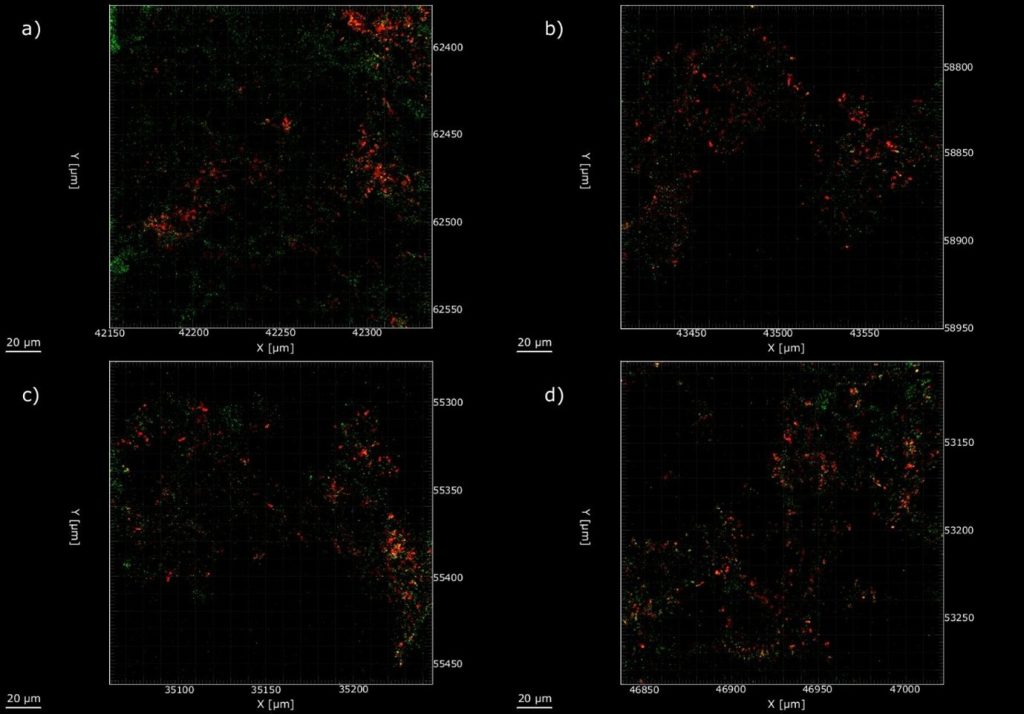
Figure 8. Confocal microscopy of biofilm formed over UNS G10180 carbon steel surfaces for AR (a, b) biotic coupon sample 1; (c, d) biotic coupon sample 2, after exposure anaerobic nutrient-enriched artificial seawater media dosed bi-weekly with glutaraldehyde for 28 days.
