Paige Policelli a final year SoCoBio student is delighted to be named in a new publication.
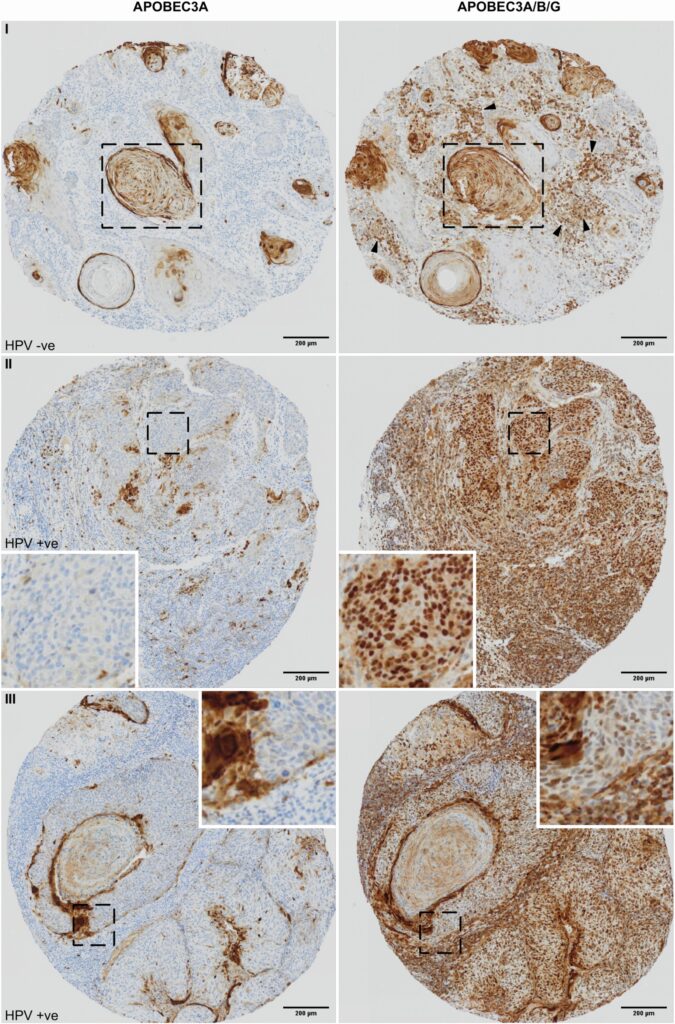
APOBEC3A and APOBEC3B are important within the human innate immune response, protecting us from viruses by inhibiting their replication. APOBEC3A and APOBEC3B deaminate cytosine residues, inducing mutations into the viral genome. However, aberrant APOBEC3A and APOBEC3B expression has been linked to somatic single-base substitutions in squamous cell carcinomas. These somatic mutations drive tumour development and can produce drug-tolerant cell populations, leading to chemotherapy resistance.
To provide insight on the regulation of these two cytidine deaminases, not just within the context of cancer, but also in normal and healthy tissue, single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) from tissues that when cancerous, display high APOBEC-mutational burden were studied. From this, it was distinguished that APOBEC3B is expressed in keratinocytes that are actively proliferating and entering mitosis, yet contrastingly APOBEC3A expression is confined to terminally differentiating keratinocytes. Analysis of biological pathways also implicated the transcription factor, Grainy-head like 3 (GRHL3) to be important for regulating APOBEC3A expression during the process of keratinocyte differentiation.
Paige used short-interfering RNA (siRNA) to knockdown GRHL3 in normal and two head and neck squamous cancer cell lines, which validated that APOBEC3A expression during keratinocyte differentiation requires GRHL3.
To summarise, the Fenton group’s publication provides new insights for the role of APOBEC3A within keratinocyte differentiation in normal tissue and provides a mechanism which can become perturbed within cancer. They used many techniques including scRNA-seq, immunohistochemistry, spatial transcriptomics and multiple functional experiments. We also identify that APOBEC3A expression within keratinocyte differentiation is dependent on the new player, GRHL3.
Link to publication: https://doi.org/10.1038/s44318-024-00298-9